No harm and pain for both mother and the baby
Benefits Of Banking
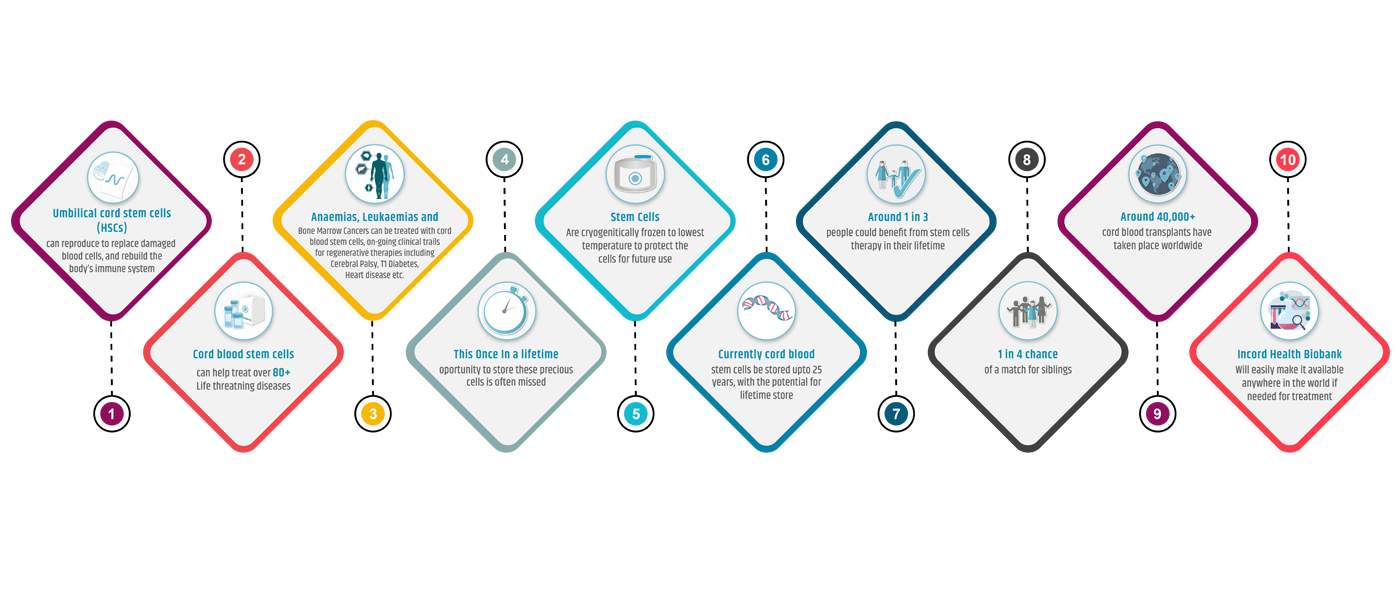
Among the many benefits of cord blood banking is the assurance that you are contributing to the prevention of more than 80 serious medical disorders. These numbers are gradually increasing every day. In addition to the current treatments, clinical trials for the use of cord blood in strokes, heart disease, diabetes, and many other regenerative therapies are currently being conducted.
In comparison to other methods of bone marrow transplantation, cord blood has proven to be favourable and advantageous. There are many reasons including all the following:
Blood can be easily collected from the umbilical cord at the same time as the cord is cut without causing any harm or pain to the mother or the baby. On the other hand, bone marrow collection necessitates an invasive surgical technique and general anaesthesia, both of which have inherent risks.

Better matching
The recipient’s stem cells must match for the transplant to be effective. Some public databases contain such matched stem cells. Transplants that use genetically similar stem cells from a blood relative are more successful. The patient preferably needs to use his own stem cells or those from a member of his immediate family if a public match cannot be obtained.
Own stem cells are always the ideal match for the individual. When it comes to compatibility, siblings have a 25% probability of being a perfect match and a 50% chance of being a partial match. Altogether, this gives siblings a 75 percent chance of being a possible match. Since each parent provides markers used in matching, parents have a 100 percent chance of being a partial match. As a result, a child’s cord blood stem cells may one day be used to treat the mother or father of the child. The decision on how close a match must be in order to undertake a transplant ultimately rests with the doctor.
Less risk of post-transplant complications
Apart from being more readily accepted by the body, cord blood stem cells have a considerably lower risk of developing graft-versus-host disease after transplant (GVHD). GVHD occurs when the body is attacked by the transplanted cells. It’s a significant issue with stem cell transplantation. The National Institute of Health states that the relationship between the donor and the recipient affects the risk of GVHD following a stem cell transplant:
Identical twins: very low chance of suffering from GVHD
Blood-related family members: 35%–45% chance of GVHD
Unrelated: 60%–80% chance of GVHD
Better HLA Type / Matching
Own stem cells are always the ideal match for the individual. When it comes to compatibility, siblings have a 25% probability of being a perfect match and a 50% chance of being a partial match. Altogether, this gives siblings a 75 percent chance of being a possible match. Since each parent provides markers used in matching, parents have a 100 percent chance of being a partial match. As a result, a child’s cord blood stem cells may one day be used to treat the mother or father of the child. The decision on how close a match must be in order to undertake a transplant ultimately rests with the doctor.
Part of this better acceptance by the body is because cord blood stem cells have rarely been contaminated with latent viruses. For stem cells from different sources, this is not the case. Since they haven’t been exposed to any diseases, cord blood stem cells have earned the title “privileged.”
HLA typing is used to discover a matching donor for stem cell transplants.
Special proteins called HLA Markers are found in human leukocyte antigen. These marker helps the immune system to recognise which cells belong to you. When the patient’s HLA and the donor’s HLA closely match, transplants are highly successful.
- A test like a blood grouping test but much more complex
- Immediate family is the first source of donors as HLA markers are inherited from parents
- 4 out of 6 HLA match (~67%) between the patient & the donor is sufficient for cord blood stem cell transplant
- ½ of your HLA markers are inherited from father and ½ from mother, so a match is difficult for any of the parents
- Siblings have a 25% chance of being a full match.
- 70% of Indian patients DO NOT find a match in their family
Some Advantages Of Cord Blood Banking
Include The Following:
- More people can receive stem cells from cord blood than from bone marrow. This is because the cord blood does not have to match that of the person receiving the transplant as closely as with a bone marrow transplant.
- There is less chance of a person’s body rejecting the stem cells from cord blood than from bone marrow.
- Cord blood stem cells may support the immune system during cancer treatments. People cannot use stem cells from bone marrow in this way.
- Collecting cord blood is very easy and no risky at all for the donor than collecting bone marrow.
- The collection of cord blood poses no risk to the new-born or the person giving birth.
- Cord blood banks can freeze and store cord blood, which means that it is ready for use when needed.
- Donations to a public cord blood bank is free.
- Donations to public cord blood banks may help save the lives of others.
What Is Cord Blood Banking Used For?
Stem cells found in cord blood can save lives. Patient who needs stem cell transplants can be benefited from the baby’s cord blood. After being transplanted into those patients, stem cells aid in the production of fresh and healthy cells. Stem cell transplants can benefit patients from the:
- Cancers like leukaemia and lymphoma.
- Bone marrow diseases requiring a transplant.
- Anaemias like sickle cell disease.
- Certain immune system disorders.
- Metabolic Disorders like Hurler syndrome | Tay-Sachs Disease | Krabbe disease
Since it has been used successfully in transplant medicine for more than 30 years, cord blood can be utilised to treat more than 80 critical medical conditions.
In recent years, the use of cord blood has increased in regenerative medicine clinical trials for disorders like Autism, Cerebral Palsy, Type 2 diabetes, and cardiac ailments that were formerly thought to be incurable.
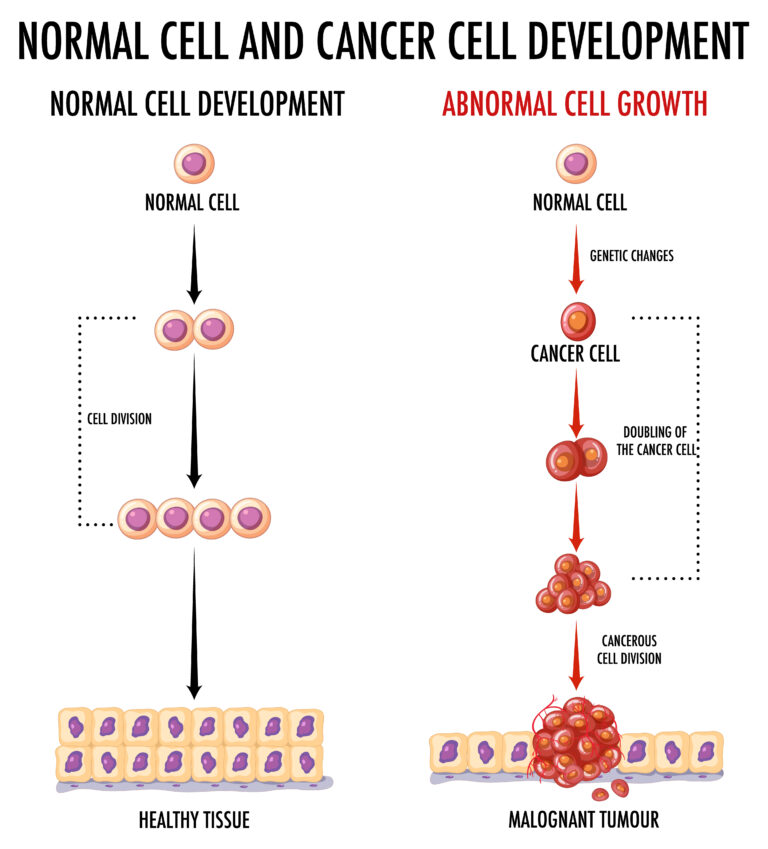
In Today’s Modern World, Stem Cells Are Used In The Treatment Of more than 80 Critical Medical Conditions, Gradually Growing Day By Day.
Click here for List Of Application Using Cord Blood Stem Cells In Medicine

